And also because... I haven't searched yet the notes for algae. I have searched for fungi notes though, but today, we were actually going to learn about algae first. That made me restless. Haha. I was afraid if Dr. Wan suddenly asked me about algae (which I have no notes on it nor read anything about it beforehand) so... I'm deeply terrified if i was asked. Hehe. And it was all because... the night before, I used all night to study for my SKP test x'D So I guess I am worried about my SKP after all~~
Today we continue our lesson with algae. And to be in class without reading the notes first is so not cool. By 'not cool', I mean I am not able to discuss about it with the whole class since everyone seemed to have read about it and I don't. I was completely clueless. Hmmm. So I will be updating this blog while learning about algae all over again. By the end of the blog I should have understand about algae, and what you guys are actually talking about during class x'D
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ALGAE
- Eukaryotes
- Most algae are photosynthetic (carry out photosynthesis) and some are chemoheterotrophic (obtain energy from chemical reactions and nutrients from preformed organic matters).
- Can be unicellular or multicellular.
- Can occur in salt or fresh water, or on the surfaces of moist soil or rocks.
- Reproduction in algae occurs in both sexual and asexual forms.
- Major suppliers of food and oxygen within the aquatic communities.
- Algae form the base of aquatic food chain.
 |
| Algae covering water surface. |
 |
| Volvox ; a type of algae |
 |
| Algae covering surface of rocks. |
GROUP OF ALGAE
Chlorophyta (Green algae)
- Occurs in freshwater and some live in the sea.
- Most are single cells and microscopic.
- Consists about 7,000 species.
- Store food in the form of starch.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and b, accessory pigments : carotenoids and xanthophyll.
- Example : Ulva (sea lettuce), Codium sp. (dead man's finger)
.jpg) |
| Ulva |
 |
| Codium sp. |
Phaeophyta (Brown algae)
- Found in marine environment.
- Made up of holdfast (base used to attach to rock or bottom), pneumatocyst (air bladder to aid buoyancy) and stipe (supporting stalk) and blade (leaflike structure that floats on the surface to collect sunlight for photosynthesis).
- Cell walls made up of cellulose and polysaccharides called "alginic acid".
- Store food in the form of "laminarin".
- Consists about 1,500 species.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and c, accessory pigments : xanthophyll and fucoxanthin.
- Example : Fucus spp. and Sargassum spp.
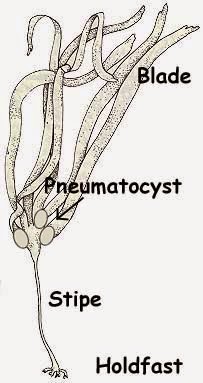 |
| Structure of brown algae |
 |
| Sargassum spp. |
 |
| Fucus spp. |
Rhodophyta (Red algae)
- Mainly live in shallow waters and deep tropical seas. Few occurs in freshwater.
- Most common in warm-temperate and tropical climates.
- Consists about 4,000 to 6,000 species.
- Lack flagella.
- Store food in the form of "floridean starch".
- Cell walls are made up of cellulose and polysaccharides such as agar and carrageenin.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and d, accessory pigments : carotenoids, xanthophylls, phycobilins.
- Example : Porolithin sp., Kappaphycus
 |
| Kappaphycus |
 |
| Porolithin sp. |
Euglenaphyta (euglenoids)
- Occurs in freshwater.
- Protozoa-like algae.
- Flagellated.
- Store food in the form of "paramylon".
- Some are photosynthetic and some are heterotrophic.
- No cell wall.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and b, accessory pigments : carotenoids and xanthophylls.
 |
| Structure of euglenoids |
 |
| Examples of euglenoids |
Chrysophyta (golden algae)
- Occur in both marine and freshwater.
- Flagellated.
- Cell walls are made up cellulose and pectin (which often filled with silica).
- Store food in the form of "leucosin" and also in oil droplets.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and c, accessory pigments : carotenoids, fucoxanthin, xanthopylls.
 |
| A colony of golden algae. |
Dinoflagellates (Phylum Pyrrophyta)
- Occurs in both marine and freshwater.
- Some are photosynthetic, some are heterotrophic.
- Have two flagella. (whip, turn and maneuver in water).
- Store food in the form of starch.
- Some species of dinoflagellates emit blue light when disturbed, called bioluminescence.
- Some species of dinoflagellates are toxic and can cause red tides and shellfish poisoning.
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and c, accessory pigment : carotenoids
- Example : Noctiluca scintillans, Pfiesteria piscicidia
 |
| Noctiluca scintillans |
 |
| Pfiesteria piscicidia (SEM) |
 |
| Bioluminescent algae |
 |
| Red tides (a type of harmful algal bloom) |
Bacillariophyta (diatom)
- Occurs in freshwater, salt water, moist soil and moist surface of plants.
- Often regarded as the most beautiful algae.
- cell walls are made up of glass that is very finely etched with a species-specific pattern of dots and lines.
- Store food in the form of chrysolaminarin (oily carbohydrate).
- Contains primary pigments : chlorophyll a and c, accessory pigments : carotenoids, fucoxanthin.
USES OF ALGAE
Algae are used in food, animal feed, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels. They can also be used for carbon sequestration and bioremediation of waste and waste water. (this is what I found when I Google for the uses of algae).
While... These are the points when we discussed in class that day. Algae are used as food (seaweed), fuel, collagen (cosmetics), fertilisers, polisher, filtration and dye for textiles (clothes).
#FUNFACT
> Why protist is not classified as "Plantae"?
Because they don't have vascular system like in plants.
> Why protist is not classified as "Animal"?
Because they are autotroph (photosynthetic).
Soooo, like I said before, by the end of the blog. I should have learned something about algae. And... I did learnt something (about algae) while finishing this journal! ฅʕ•̫͡•ʔฅ
P/S Somehow this update is more about me learning about algae instead of what I did in class that day. I'm so sorry. x'D
Until next class. Hehe.
And happy holiday~~~
Adieu!

No comments:
Post a Comment